
In inner ear lesions, vertigo is often more severe.Generally, symptoms include ear pain, fullness, vertigo, hearing loss.Submersion Injury: includes drowning, near drowning.

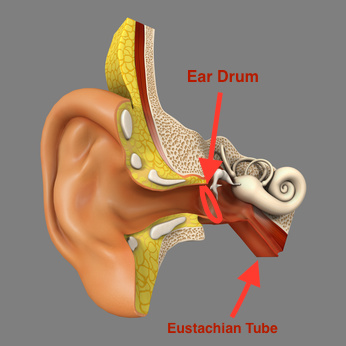
Immersion Pulmonary Edema: also termed swimming induced pulmonary edema.Decompression Sickness: Dissolved nitrogen comes out of solution, forms bubbles in blood and tissue ("the bends").Pulmonary Barotrauma: occurs when diver breathing compressed air ascends too rapidly.Caustic Cocktail: Inhalation of absorbent material used to scrub CO2 mixes with water.Carbon Monoxide Toxicity: CO toxicity typically results from a faulty air compressor.Hypothermia: decrease core temperature with prolonged exposure to cold water.Nitrogen Narcosis: toxic effects of breathing nitrogen-containing gases while at depth.Oxygen Toxicity: harmful effects of breathing oxygen at higher partial pressures than normal.Barodentalgia: trapped dental air causing squeeze.Mask Squeeze: air in the mask decreases in volume during a dive, creating negative pressure.Pressure difference between middle ear, inner ear can rupture oval or round windowĭifferential Diagnosis Differential Diagnosis Dive Medicine.Results from forceful Valsalva against eustachian tube.Most concerning form of otic barotrauma can have permanent effects.Water may rush into the ear, causing a cold caloric stimulus (nausea, disorientation, balance dysfunction).Sudden relief of pain suggests TM has ruptured.Without equalizing, pain will worsen during descent.At 2.67 PSI, the Eustachian tube is squeezed closed by the pressure gradient between the sinuses.The greatest changes occur in the first few feet of diving (1.78 PSI at 4 FSW, 2.67 PSI at 6 FSW).For this reason, divers are taught to equalize their ears at surface and throughout the dive.Occurs when middle ear pressure is not equalized with ambient pressure.Subsequently, there is edema, hemorrhage in the canal.Vacuum-like force develops between occlusion, tympanic membrane.Can occur during descent when external auditory canal is occluded.Patients typically present with ear related complaints (pain, fullness, vertigo, disruption in hearing, tinnitus).Barotrauma occur to external ear (EEB), middle ear (MEB) or inner ear (IEB) MEB is most common by far.First time divers experience middle ear barotrauma 30% of the timeĪnatomy of the outer, middle and inner ear.This page refers to Otic barotrauma, typically seen during scuba diving or air travel during descent.5.1 Differential Diagnosis Dive Medicine.A recently reported, novel technique for insertion of temporary tympanostomy tubes is promising but requires further evaluation. There is insufficient evidence to support the efficacy of either nasal balloon inflation or pressure-equalizing ear plugs for the prevention of otic barotrauma. However, oral pseudoephedrine (1 mg/kg) does not appear to be effective in children. There is level 1 evidence that supports the efficacy of oral pseudoephedrine (120 mg) in preventing otic barotrauma in adults. This review highlights the lack of published evidence relating to what is a significant and increasingly common problem in otology. Data Extraction:Īrticles and data were extracted and analyzed according to Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses and other international guidelines. Outcomes of interest were reduced severity or the successful prevention of otic barotrauma in participants undergoing gradual changes in pressure during air travel or its simulation.
Study Selection:Įnglish language articles including more than or equal to five participants or cases were included.
BAROTRAUMA OTIC FULL
Ten databases including Embase, MEDLINE, the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials were searched using the full historical range. In particular, this review sought to identify procedures, techniques, devices, and medications for the prevention of otic barotrauma as well as evaluate the evidence relating to their efficacy. To conduct a systematic review of the published evidence relating to the prevention of otic barotrauma in aviation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
